 Project Life Cycle
Project Life Cycle

Recommended templates
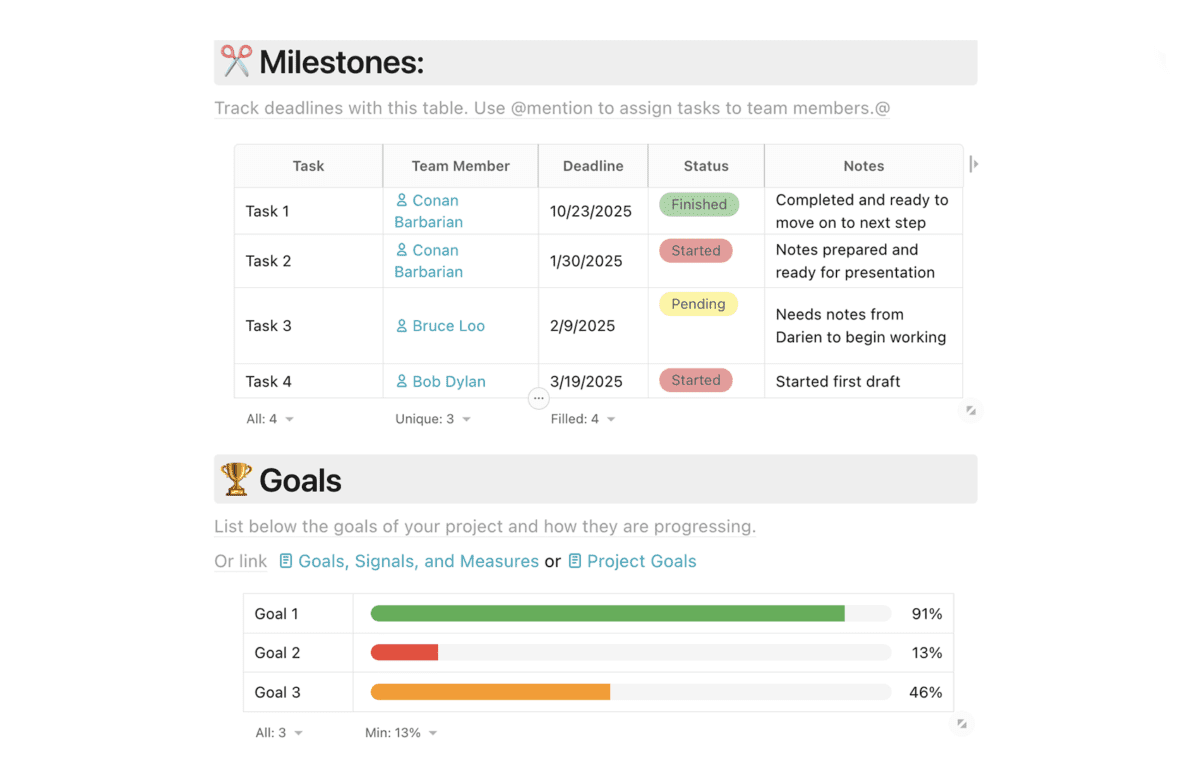
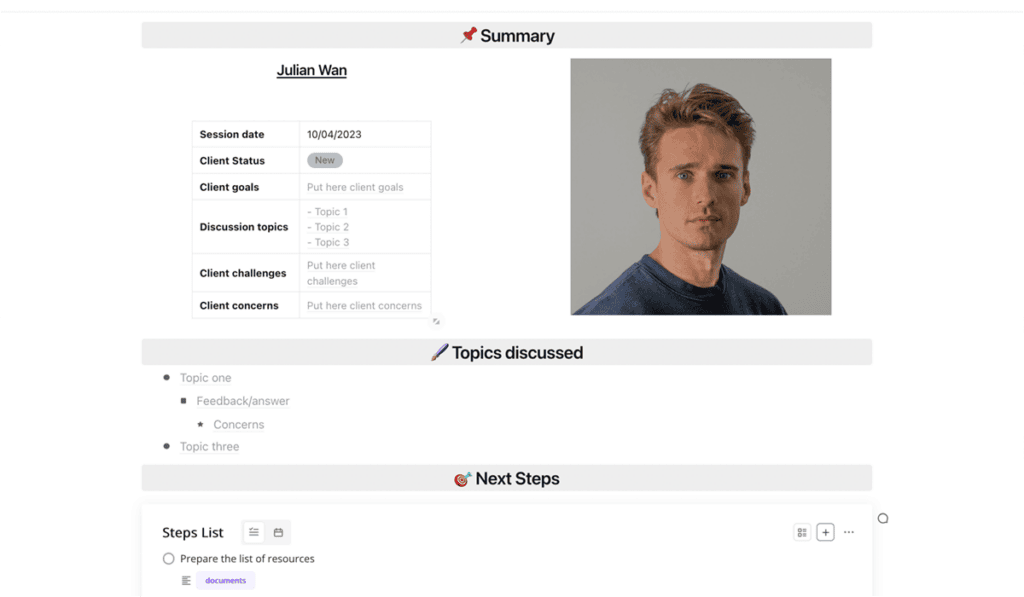
Coach's Notes
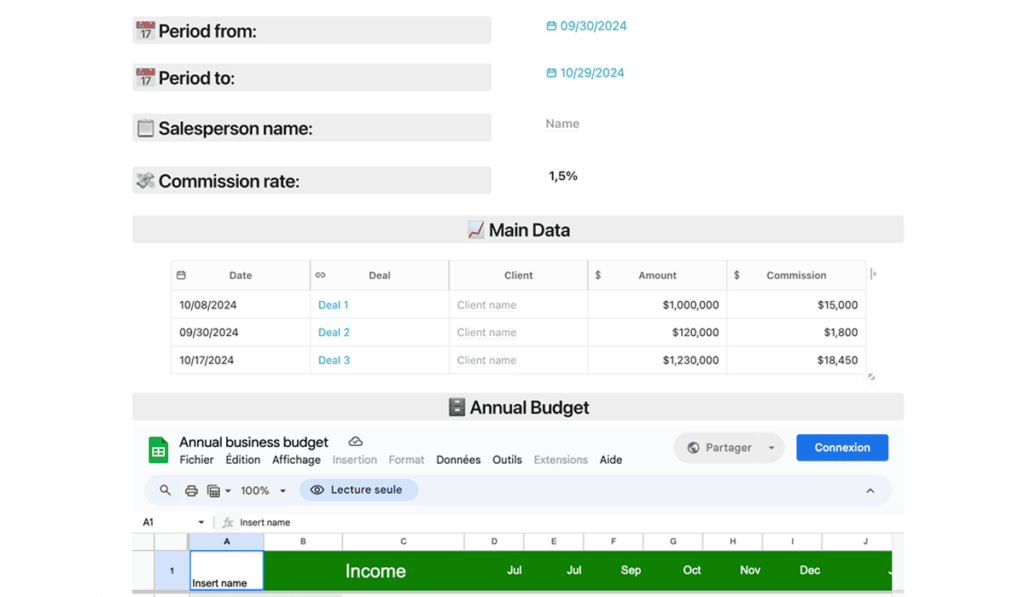
Commission Split Sheet
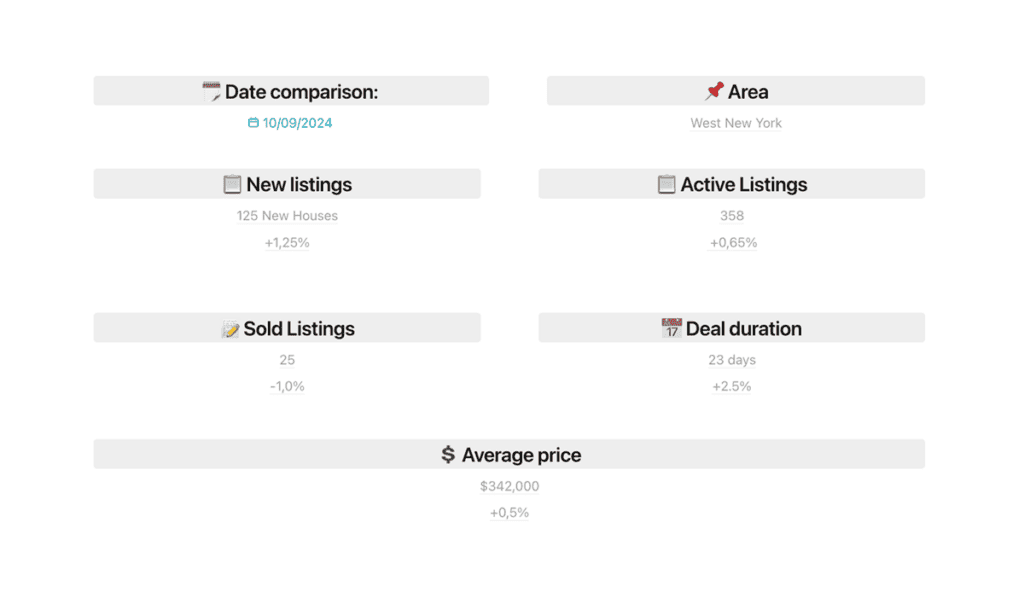
Local Market Update
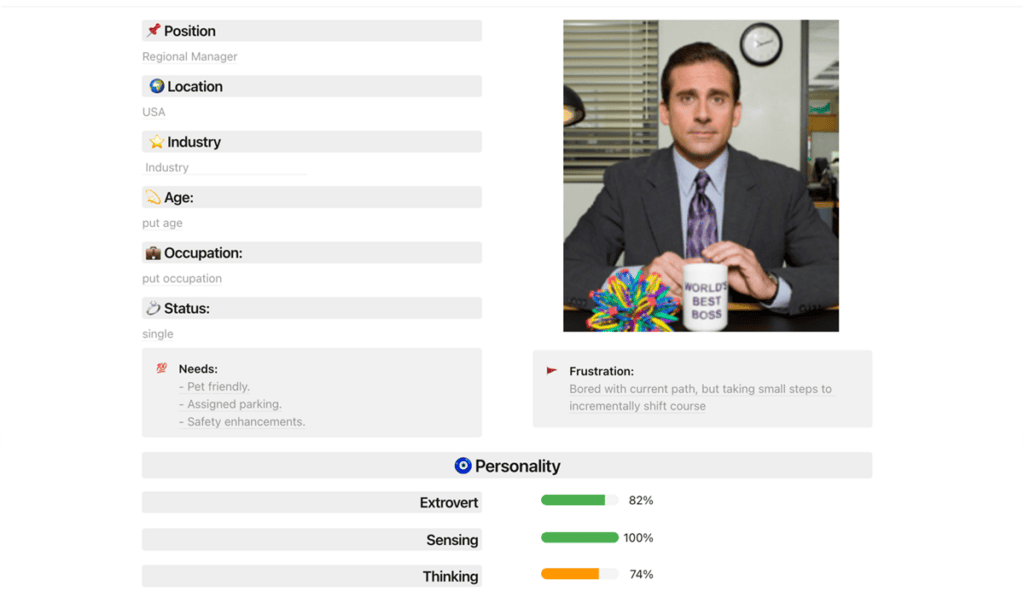
Real Estate Buyer Persona Profiles
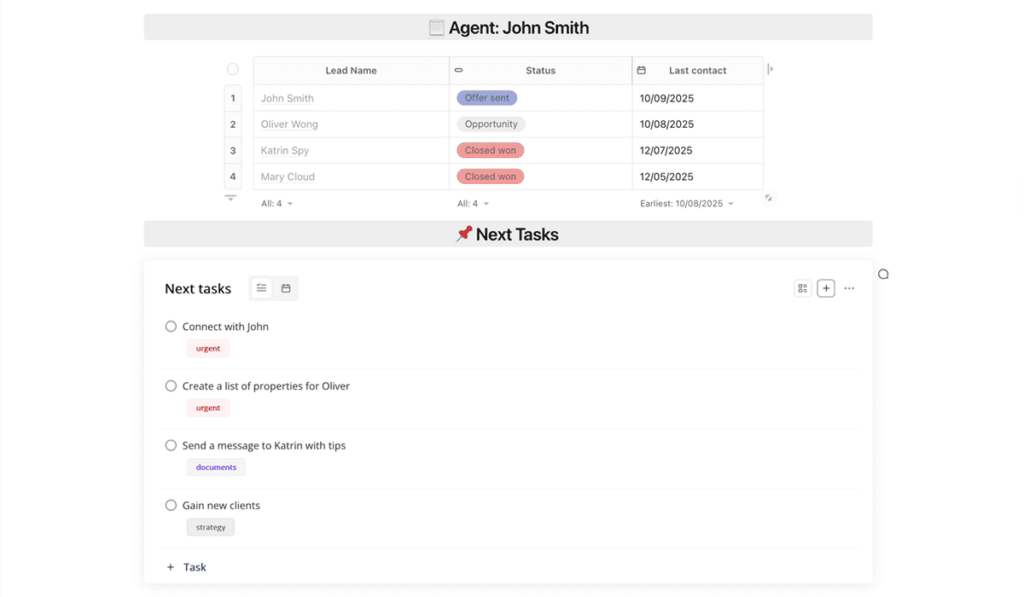
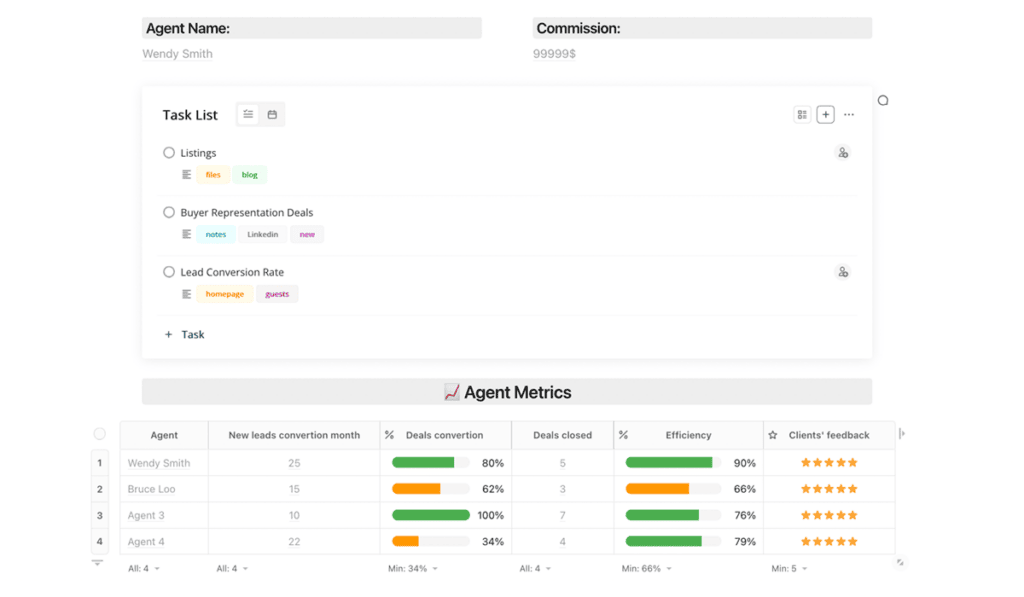
Agent Scorecard
Market Comparables

Buyer Leads Report